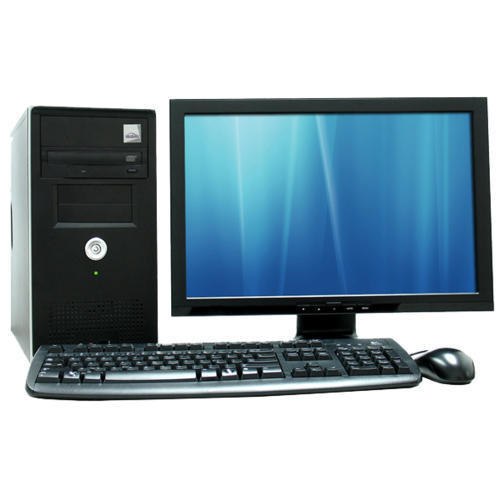
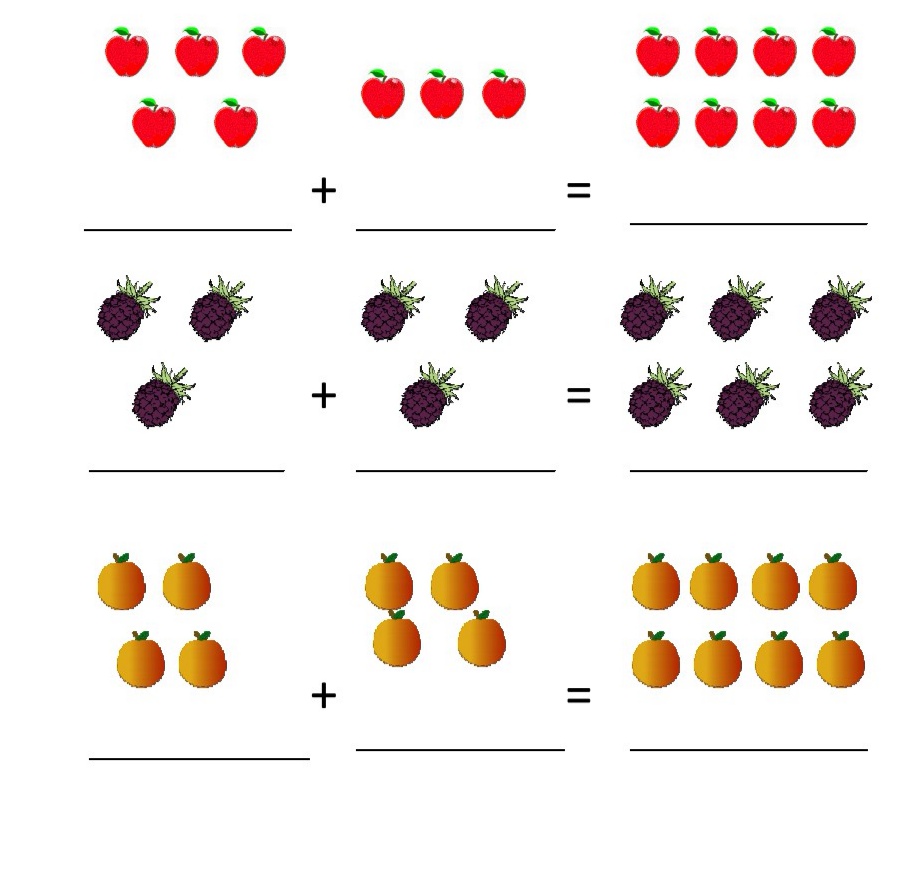
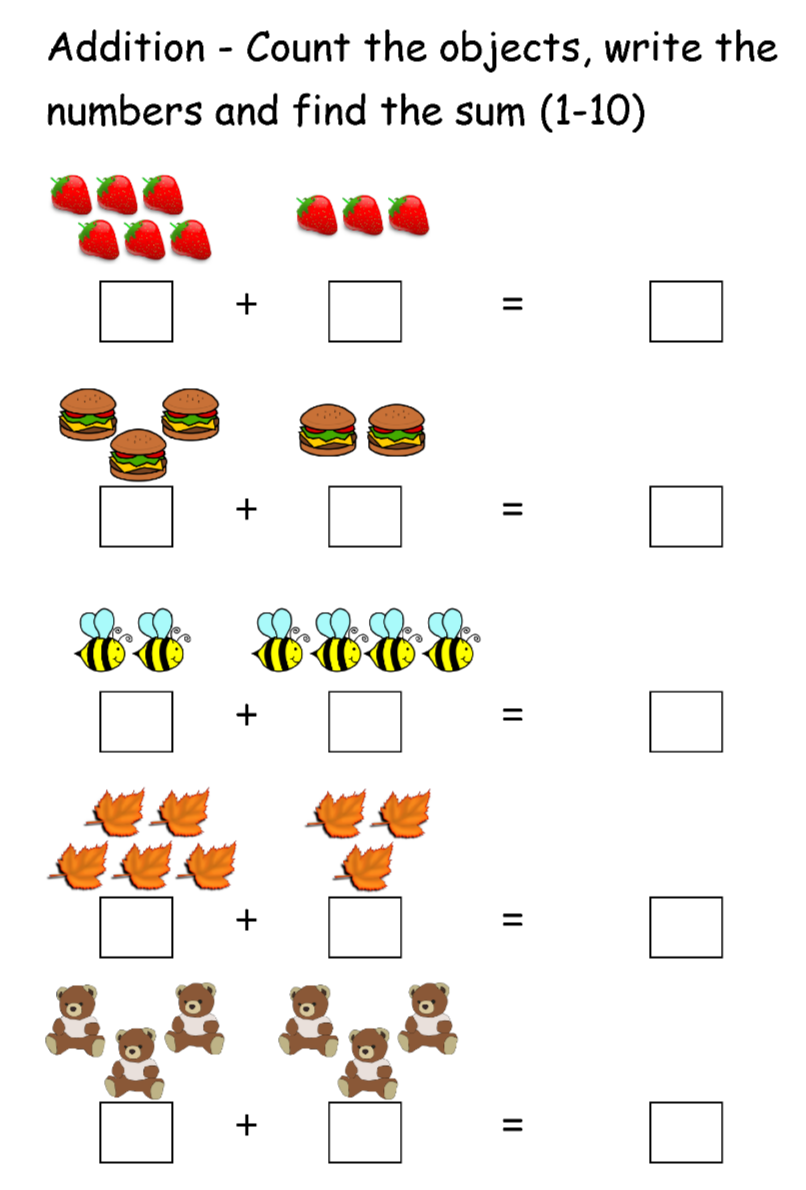
கற்றுக்கொள்பவை:
- கணினி என்றால் என்ன?
- கணினியின் வகைகள்
- இன்புட் மற்றும் அவுட்புட் என்றால் என்ன?
- அப்ளிகேஷன் என்றால் என்ன?
- மெமரி டிவைஸ் என்றால் என்ன?
கணினி என்றால் என்ன?
கணினி என்பது உள்ளீட்டிற்கு (Input) உதவுவது மற்றும் வெளியீட்டை (output) வழங்கும் மின்னணு இயந்திரம் ஆகும்.
கணினி “சார்லஸ் பாபேஜ்” என்பவரால் கண்டுபிடிக்கப்பட்டது .இவரே கணினியின் தந்தை என அழைக்கப்படுகிறார்.
இது தரவுகளை உள்ளிடவும் (input), அதை செயலாக்கவும் (CPU), அதை சேமிக்கவும் (memory) மற்றும் முடிவுகளை வெளியிடவும் உதவும் சாதனங்களால் ஆன இயந்திரம்.
கணினியின் பயன்பாடுகள்:
- அதிக வேகத்தில் கணக்கிட உதவுகிறது.
- எக்ஸ்ரே ஸ்கேன் போன்ற மருத்துவ வேலைகள் செய்ய கணினி உதவுகிறது.
- தகவல் பரிமாற்றத்திற்கு இணைய-கணினி (Internet) உதவுகிறது.
- இது உலகெங்கிலும் உள்ள மக்களுடன் நம்மை இணைக்கிறது.
- விளையாடுவதற்கும், இசையைக் கேட்பதற்கும், இணையத்தை அணுகுவதற்கும், திரைப்படங்களைப் பார்ப்பதற்கும், மற்றும் கணக்கீடுகளைத் தீர்ப்பதற்கும் ஒரு கணினி பயன்படுத்தப்படுகிறது.
- கல்வித்துறையில் கணினியின் பங்கை யாரும் மறுக்க முடியாது.
Computer consists of:
கணினி வன்பொருள் ( hardware ) மற்றும் மென்பொருள் (software) கூறுகளைக் கொண்டுள்ளது.
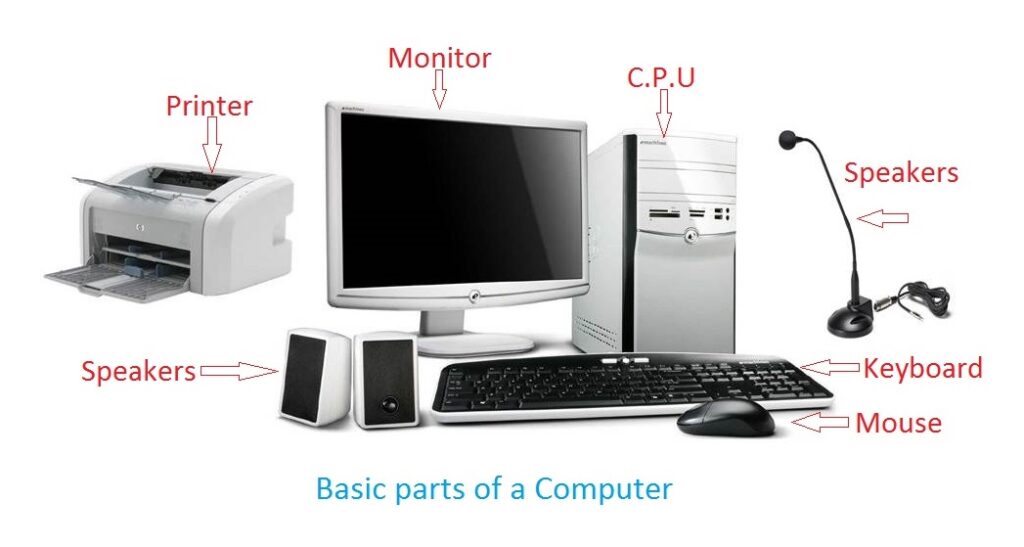
வன்பொருள் ( hardware )
இவை வெளியில் காணக்கூடிய மானிட்டர், சுட்டி ( mouse), விசைப்பலகை ( keyboard), speaker போன்றவற்றால் ஆனது.

மென்பொருள்
இது கணினியில் பணிகளைச் செய்யும் வழிமுறைகளின் தொகுப்பாகும்.
keyboard , மவுஸ் போன்ற உள்ளீட்டு சாதனங்கள் கணினியில் தகவல்களை வைக்க உதவுகிறது.
இது வெளியிலிருந்து பயனாளர்கள் தரும் தகவல்களை ஏற்று பதில் அளிக்கிறது.
கணினியின் பாகங்கள்

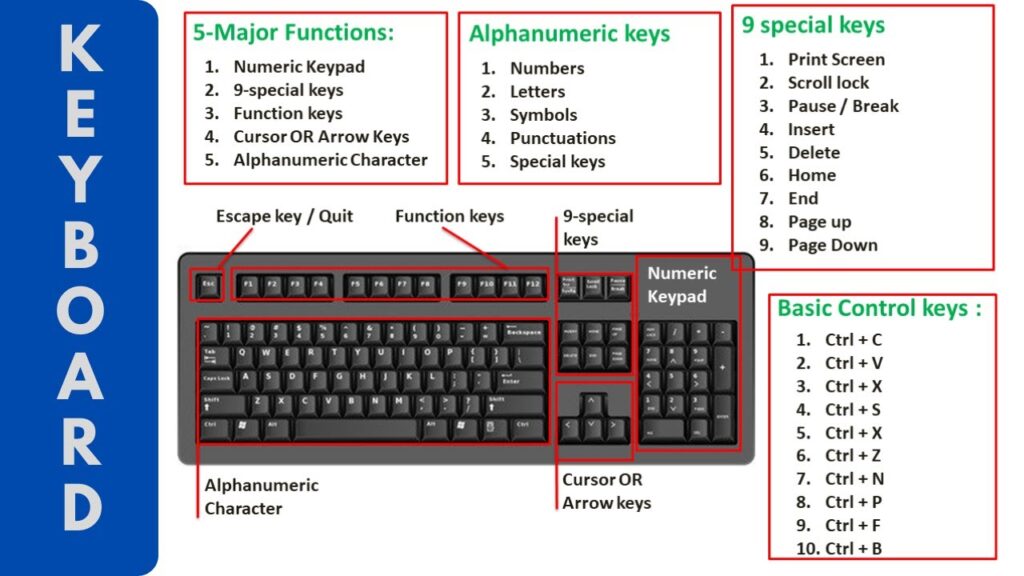
keyboard
விசைப்பலகை மிகவும் பொதுவான உள்ளீட்டு வன் பொருள் ( hardware) சாதனம்.
விசைப்பலகையில் எழுத்துகள், வார்த்தைகள் மற்றும் எண்களைத் தட்டச்சு செய்வதன் மூலம் தரவு உள்ளீடு செய்யப்படுகிறது. இது ஒரு கணினியில் தரவை உணர முடியும் மற்றும் அதிலிருந்து எந்த தகவலையும் பெறாது
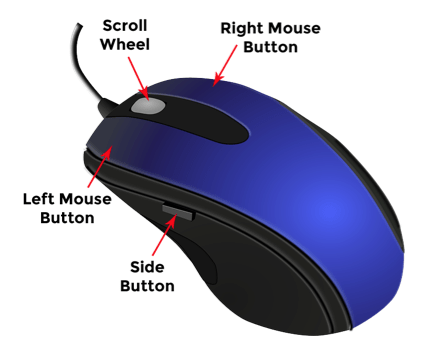
Mouse
சுட்டி ஒரு சுட்டி சாதனம்.
திரையில் உள்ள கர்சரின் இயக்கத்தை நாம் இதன் மூலம் கட்டுப்படுத்தலாம்.
மவுஸில் இழுவை விருப்பத்தைப் பயன்படுத்தலாம்.இதன் மூலம் மேலே ஸ்க்ரோல், ஸ்க்ரோல் டவுன் பண்ண முடியும்.
டக்ளஸ் ஏங்கல்பார்ட் என்பவரால் mouse கண்டுபிடிக்கப் பட்டது.
Output devices
அவுட்புட் சாதனம் என்பது கணினியிலிருந்து தரவைப் பெற்று அந்தத் தரவை வேறொரு வடிவத்திற்கு மாற்றும் வன்பொருள்.
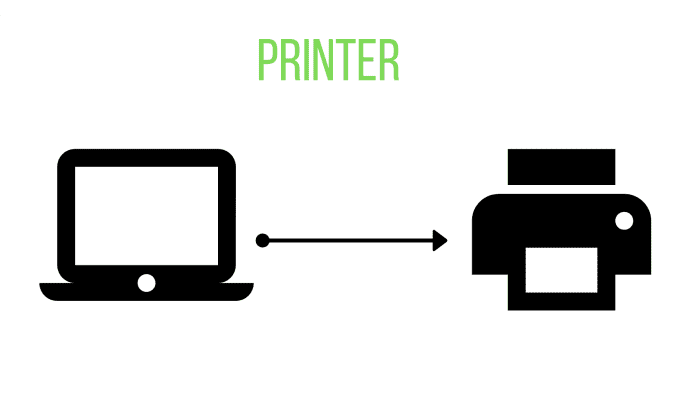
அச்சு பொறி (Printer)
வெளியீட்டு சாதன அச்சுப்பொறியிலிருந்து பெறக்கூடிய உள்ளீட்டு சாதன விசைப்பலகையைப் பயன்படுத்தி கணினியில் தட்டச்சு செய்கிறது.
கணினியிலிருந்து காகிதத்திற்கு தரவை மாற்றுவதற்கு அச்சுப்பொறி பயன்படுத்தப்படுகிறது.
வண்ண அச்சுப்பொறிகள்
கருப்பு மற்றும் வெள்ளை பிரிண்டர்கள் உள்ளன.
பல்வேறு வகையான அச்சுப்பொறிகள் டாட் மேட்ரிக்ஸ் பிரிண்டர்கள், இன்க்ஜெட் பிரிண்டர்கள் மற்றும் லேசர் பிரிண்டர்கள் உள்ளன

Touch Screen
திரையில் காட்டப்படும் படங்கள் அல்லது சொற்களைத் தொடுவதன் மூலம் பயனர் கணினியுடன் தொடர்பு கொள்ள அனுமதிக்கிறது.
வெளியீட்டுத் தகவலைத் திரையில் காட்டுவதற்கும், திரையில் உள்ள சொற்கள் அல்லது படங்களைத் தொட்டு உள்ளீடு செய்வதற்கும் தொடுதிரைகள் பயன்படுத்தப்படுகின்றன.

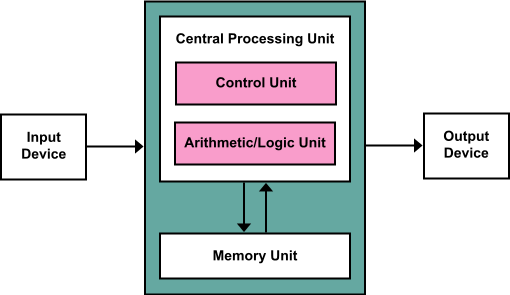
Central Processing Unit(CPU)
இது கணினியில் காணப்படும் மிக முக்கியமான பாகமாகும்.
இதுவே கணினியின் மூளை.
இது Control Unit and Arithmetic and Logic unit என்று பிரிக்கப்படுகிறது.
அனைத்து முக்கிய கணக்கீடுகள் மற்றும் ஒப்பீடுகள் இதன் மூலம் செய்யப்படுகின்றன, மேலும் இது செயல்பாடுகளை செயல்படுத்துகிறது மற்றும் கட்டுப்படுத்துகிறது.
Control unit
இது உள் மற்றும் வெளிப்புற சாதனங்களின் செயல்பாடுகளை இயக்குகிறது மற்றும் கட்டுப்படுத்துகிறது.
Arithmetic and logic unit
ALU என்பது நினைவகத்திலிருந்து (memory) பெறப்பட்ட உண்மையான எண்கணித செயல்பாடுகள் (எ.கா. கூட்டல், கழித்தல், பெருக்கல், வகுத்தல்) ஆகும்.
Memory devices
Memory devices என்பது நம் பதிவுகளை சேமித்து வைப்பதற்கான இடம்.
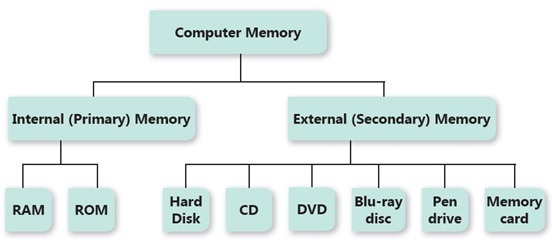
Types of memory devices
- முதல்நிலை
- இரண்டாம் நிலை
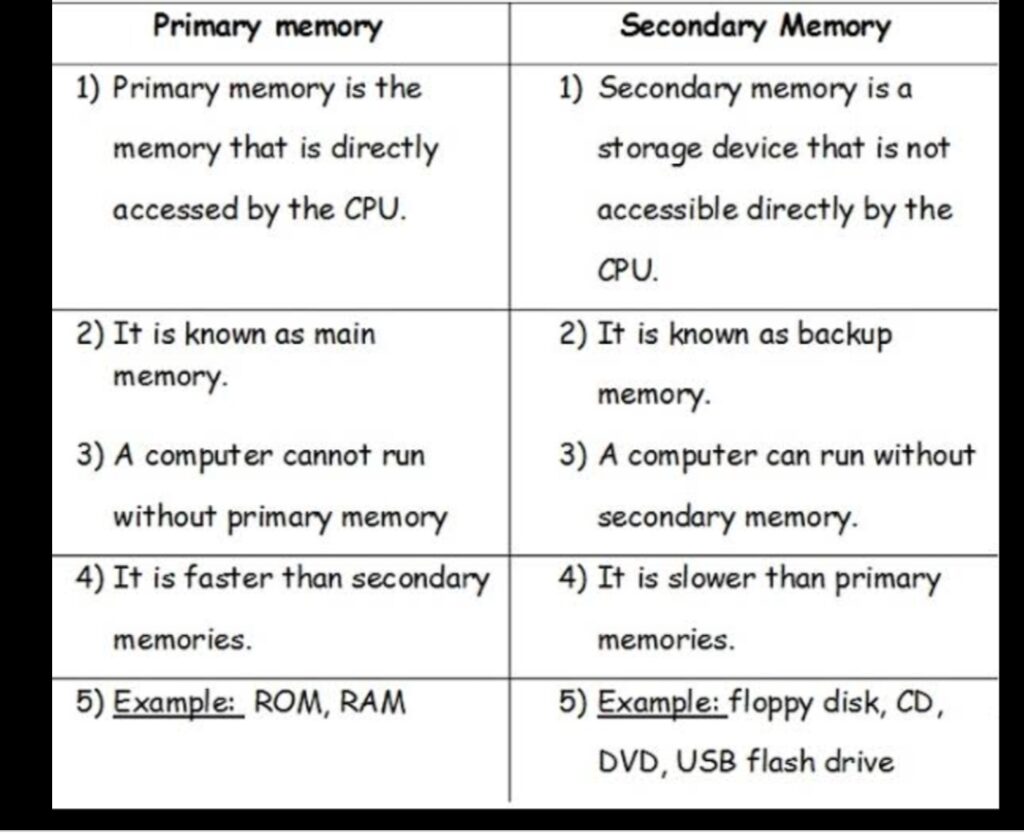
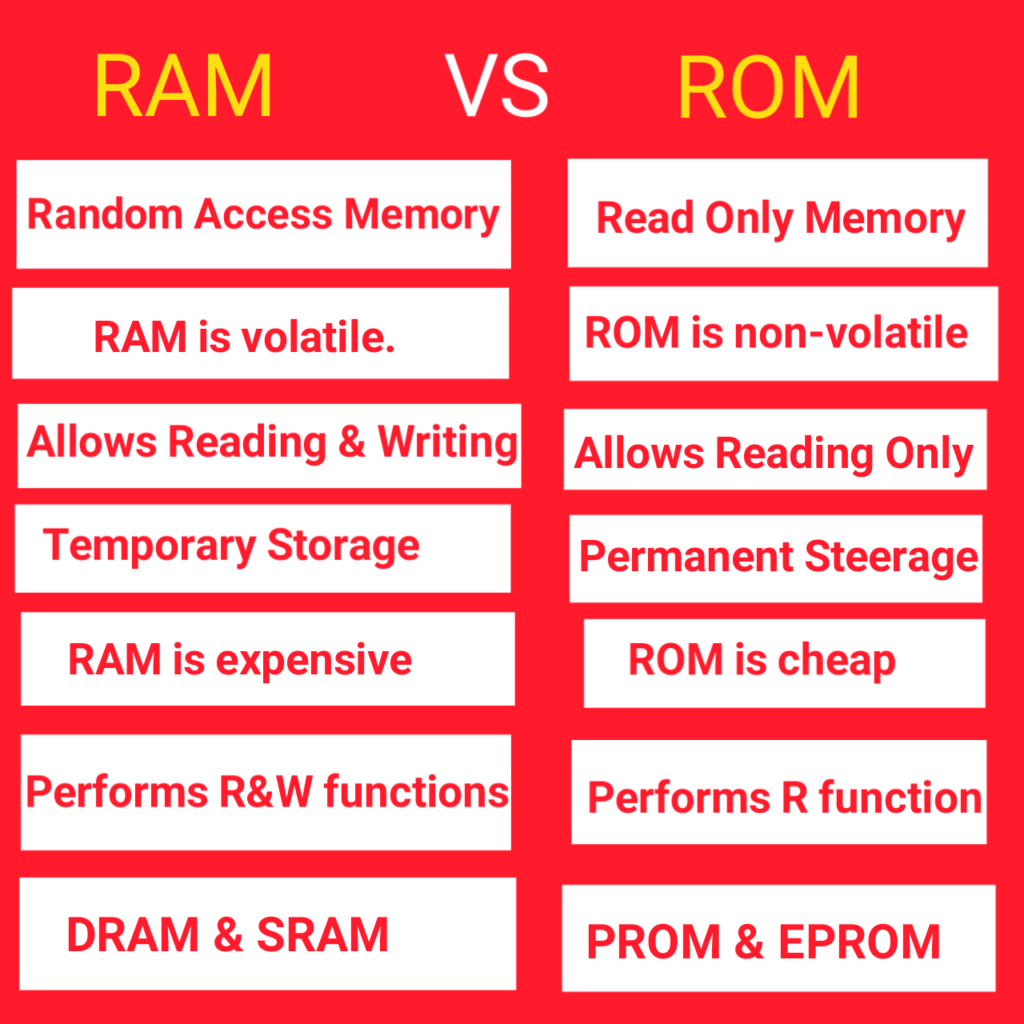
கணினி நினைவகம் என்பது கணினியில் உள்ள சேமிப்பக இடமாகும்.
இங்கு பதிவுகள் செயலாக்கப்பட்டு மற்றும் செயல்முறைகள் தொடங்கும் முன் வழிமுறைகள் பதிவு செய்யப்படுகின்றன.
Questions
1. கணினியின் தந்தை –
2. கணினியின் மூளை என அழைக்கப் படுவது –
![]()